Description
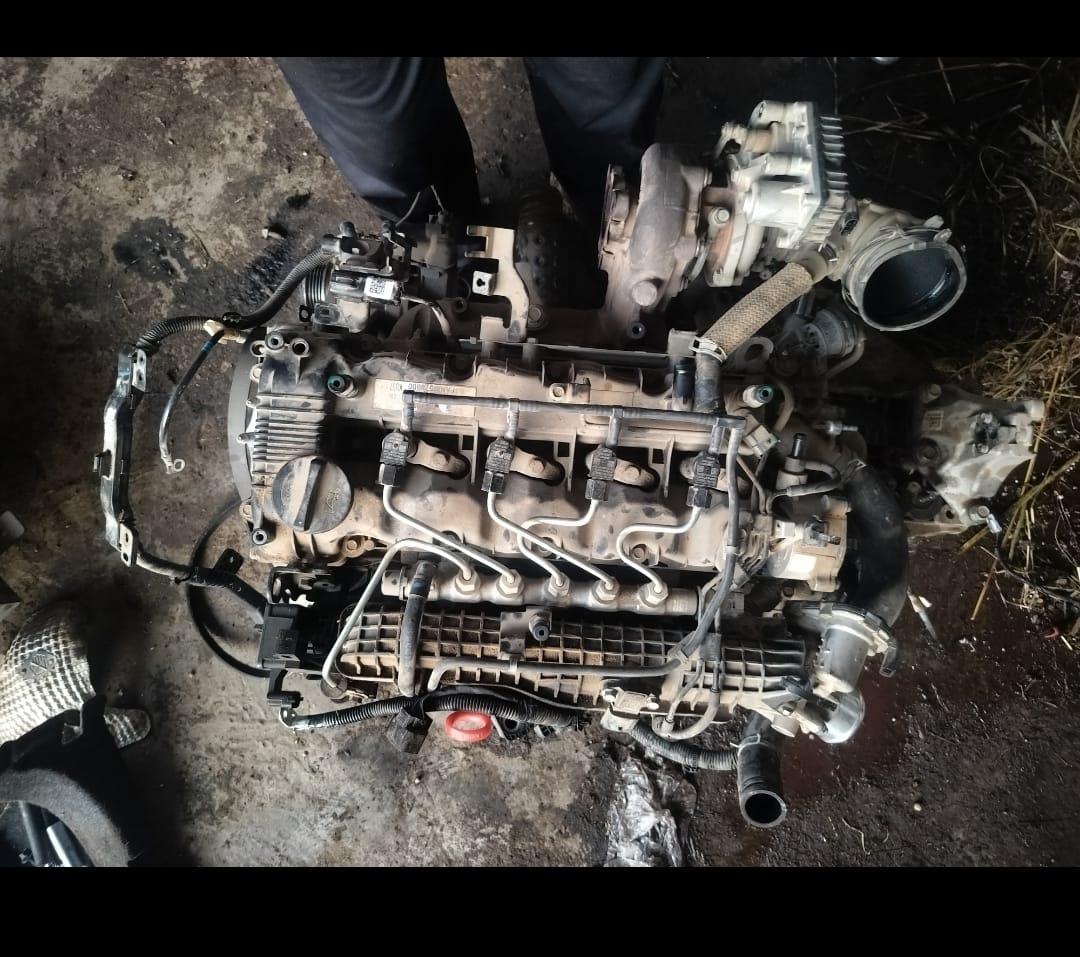
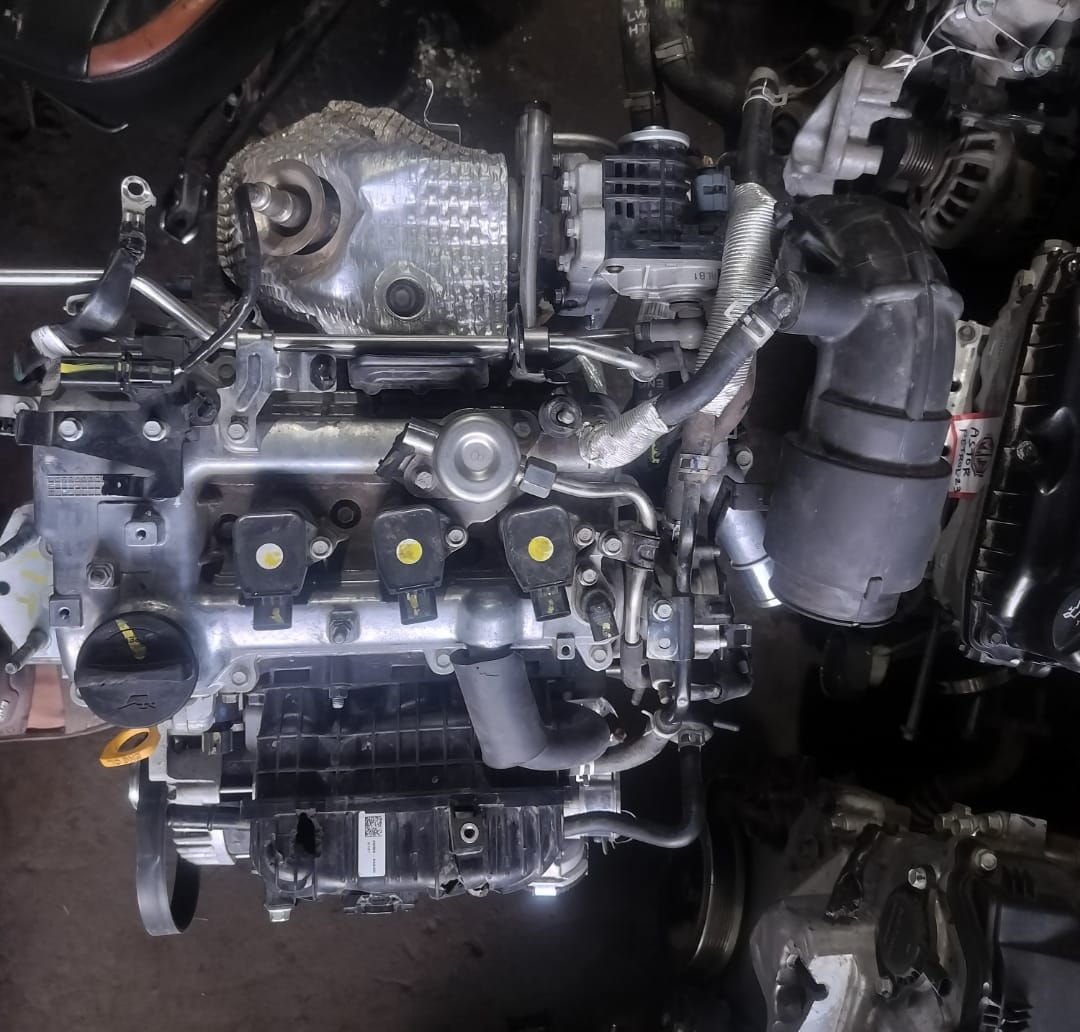
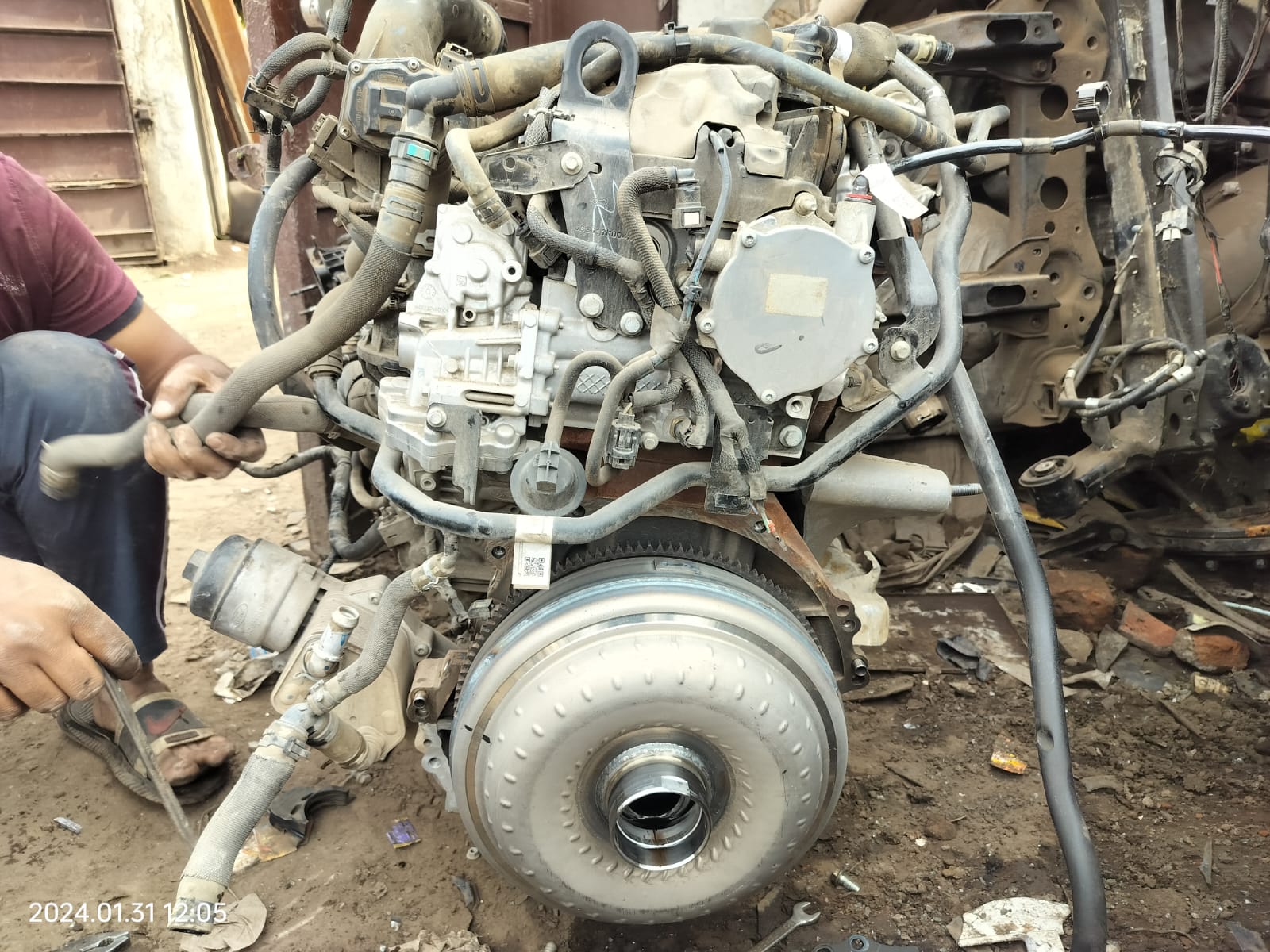
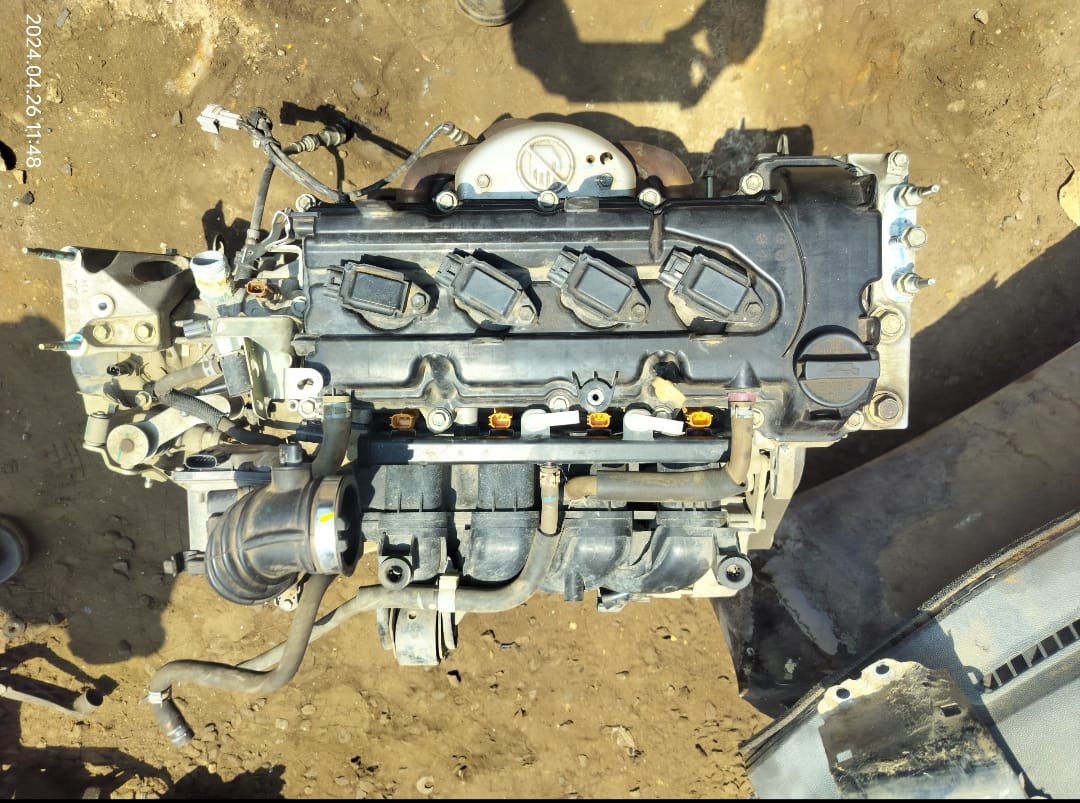
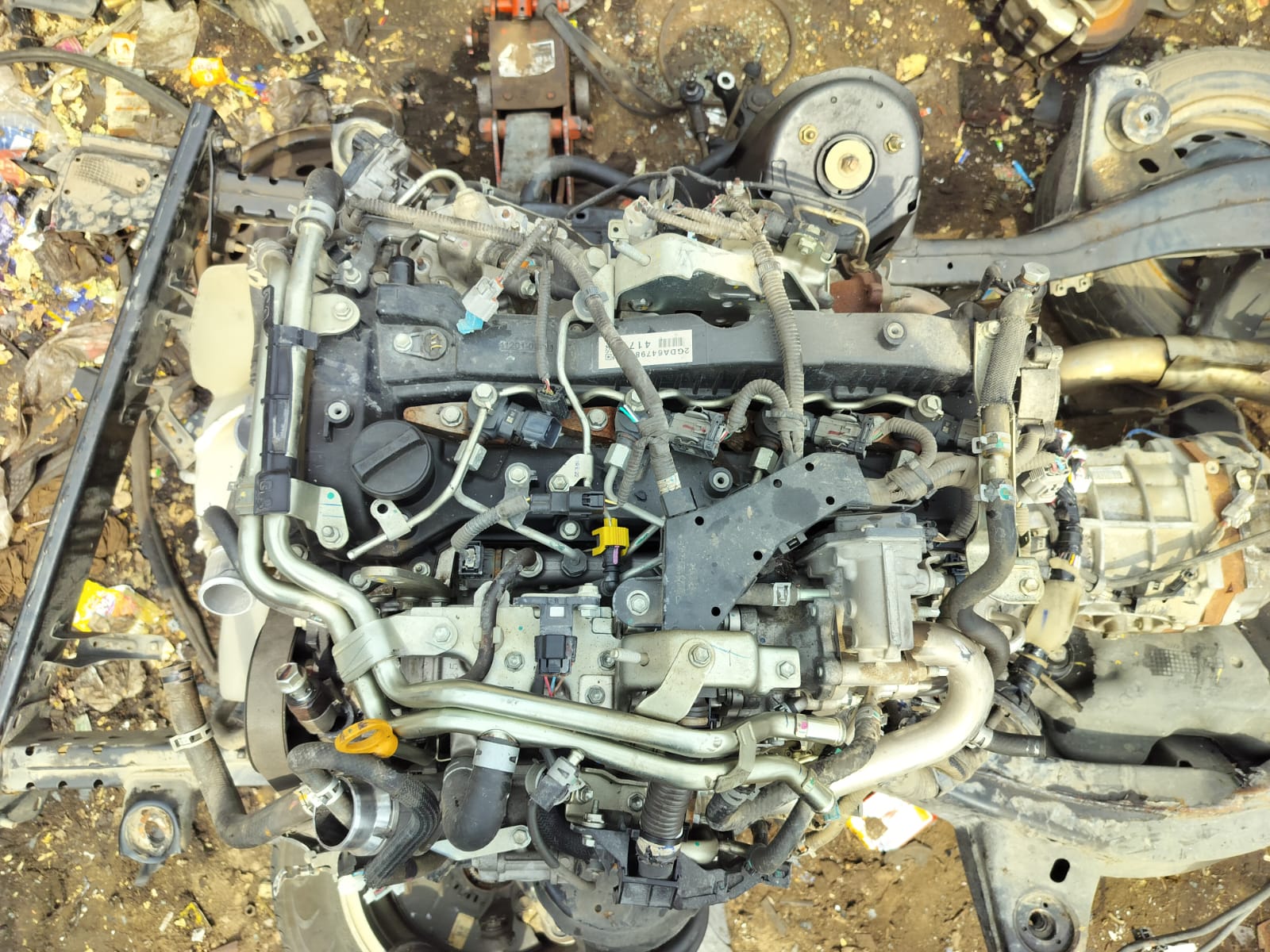
The car engine is the heart of the vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy to power the car. It typically consists of several key components, including the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, and cylinder head. Most modern cars are equipped with internal combustion engines, which are available in various configurations, such as inline, V-shaped, or flat engines.
1. *Cylinder Block:* This is the main structure of the engine, housing the cylinders in which the pistons move up and down. It is made from cast iron or aluminum to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
2. *Pistons:* These are cylindrical …
The car engine is the heart of the vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy to power the car. It typically consists of several key components, including the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, and cylinder head. Most modern cars are equipped with internal combustion engines, which are available in various configurations, such as inline, V-shaped, or flat engines.
1. *Cylinder Block:* This is the main structure of the engine, housing the cylinders in which the pistons move up and down. It is made from cast iron or aluminum to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
2. *Pistons:* These are cylindrical components that move up and down within the cylinders. The pistons are connected to the crankshaft and play a vital role in the combustion process by compressing the air-fuel mixture.
3. *Crankshaft:* The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is then transferred to the wheels to propel the vehicle forward.
4. *Camshaft:* The camshaft is responsible for opening and closing the engine’s intake and exhaust valves at the correct time. It is driven by the crankshaft through a timing belt or chain.
5. *Cylinder Head:* Mounted on top of the cylinder block, the cylinder head contains the combustion chamber, valves, and spark plugs. It seals the cylinders and allows the fuel-air mixture to enter the combustion chamber.
6. *Fuel Injection System:* Modern engines use electronic fuel injection to precisely deliver fuel to the combustion chamber, improving efficiency and performance.
7. *Turbocharger/Supercharger (optional):* Some engines are equipped with a turbocharger or supercharger to increase the engine’s power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber.
The performance of a car engine is measured in terms of horsepower and torque. Horsepower indicates the engine’s ability to perform work over time, while torque measures the engine’s rotational force. Fuel efficiency, emissions, and reliability are also crucial factors that define an engine’s overall quality.
Understanding these components and their functions is essential for anyone interested in the mechanics of how a car engine operates. This knowledge not only helps in maintaining and repairing the engine but also in making informed decisions when purchasing a vehicle.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.